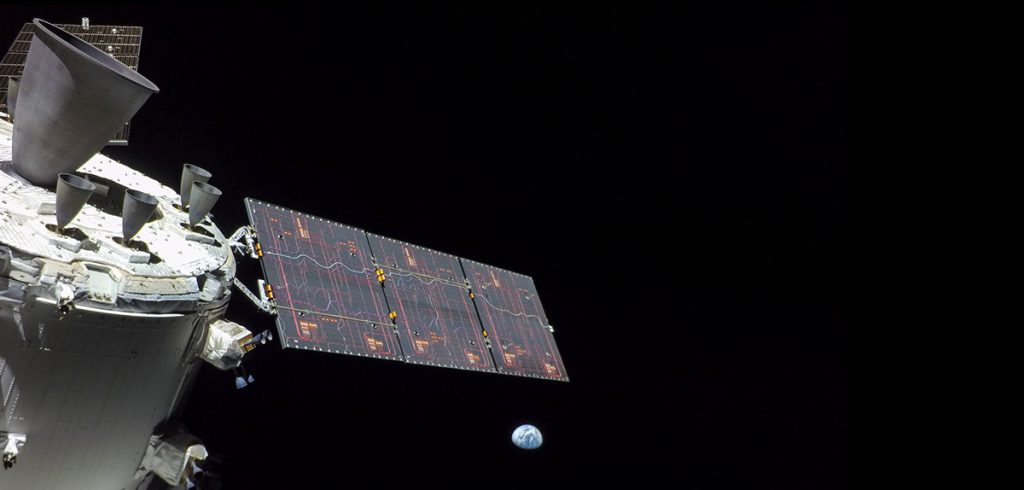
The purpose of the Artemis I mission was to test the Orion spacecraft in space for the first time. This mission was uncrewed and all systems were tested to the limit, which is vital to ensure the safety of the crew in future missions aboard the Orion capsule.
The ESM served as the main propulsion system of the Orion spacecraft, and was also used for orbital maneuvering and position control. It also provided critical life support elements—including water and oxygen—and regulates thermal conditions aboard Orion.
The Artemis I mission ended on Sunday, December 11, when Orion’s crew module splashed down in the Pacific Ocean. The part of the mission that involved the European service module came to an end just 40 minutes before splashdown, when it separated from the crew capsule and burned up, as planned, during atmospheric reentry. This marked the end of the first European service module’s long trip.
During the 25 days of flight, all systems were subject to intense testing. A myriad of sensors and cameras monitored the changes and functionalities in the systems throughout the entire mission.
It was an extremely exhausting and challenging round of tests for the Orion spacecraft. The vehicle travelled over two million kilometers, was exposed to temperatures of plus and minus 200 °C and flew at a top speed of 40,000 km/h. All systems were tested and, for the most part, they worked even better than expected.
On Sunday 11 at 18:40 CET, the long voyage ended and all tasks were successfully completed. The crew capsule splashed down safe and sound in the ocean.
While this may sound like an ending, it is but the beginning of a new era—the new journey to the Moon. Soon, we humans will fly around the Moon with Artemis II before leaving new footprints on the Moon with Artemis III.